Everyone at least once in their life has heard of platinum, for example in the field of goldsmithing and jewellery, but not everyone knows the many applications that can revolve around this element, from anticancer ones to those in favor of the environment. Before discovering them better, let's get to know this element more closely!
Platinum is a chemical element with symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It belongs to the platinum group elements series (group 10) of the periodic table of elements and is one of the rarest and most precious metals in the world. Platinum is known today for its high resistance to corrosion, to high temperatures and chemical reactivity, as well as for its catalytic and conductive properties.
The name platinum comes from the Spanish "platina", meaning "little silver", or even how “fake silver”. The name platinum was assigned to this metal by the Spaniards when they found it for the first time in Colombia in the mid-16th century.
Having clarified its properties, we can focus on its characteristics that make it so special.

Platinum is a lustrous silvery-white metal
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PLATINUM.
Platinum is a hard transition metal, thick and silvery-white with a very high melting point of 1,768°C and a boiling point of 3,825°C. It has a density of 21,45 g/cm³ and is one of the heaviest metals.
Platinum is very resistant to corrosion and tarnishing, and is insoluble in water and strong acids.
It melts, instead, in aqua regia, or a mixture composed of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. Despite its lack of responsiveness, platinum can react with oxygen at elevated temperatures to form platinum oxides.
Platinum has an electron configuration of [Car] 4f^14 5d^9 6s^1 and has a variety of oxidation states, including +2, +4 and +6. Its most common meaning is +2, but platinum can also form compounds with higher valences.
Furthermore, platinum is known for its high affinity for hydrogen and can absorb up to 900 times its volume of hydrogen under certain conditions. This property has been exploited for the development of hydrogen fuel cells, which use platinum as a catalyst for the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen to produce electricity.
BECAUSE PLATINUM IS PRECIOUS?
Platinum is one of the rarest and most precious elements on Earth, known for its many unique physical and chemical properties. Platinum is generally valued more than gold, as rarer.
What makes platinum precious are not only its rarity but also all its properties listed above and above all the extraction costs. In fact, this element has an abundance in the earth's crust estimated at 0,005 parts per million (Haynes, 2016). In 2021 the average global price of platinum has been estimated at approx 35 dollars per gram.
WHERE PLATINUM IS FOUND IN NATURE?
Platinum is found in nature mainly in the form of alloys and minerals, often associated with other platinum group metals, like palladium, born, iridium, osmium and ruthenium. Platinum deposits are unevenly distributed around the world, but the largest reserves are found in South Africa, Russia, Canada, Zimbabwe and the United States.
In particular, around 70% of the world's platinum production comes from South Africa, where the largest platinum deposits in the world are located, concentrated in the Bushveld region.
Platinum has six stable natural isotopes: 192Pt, 194Pt, 195Pt, 196Pt, 198en 200Pt, which respectively have the percentages of abundance of 0,79%, 32,9%, 33,8%, 25,3%, 7,2% and 0,01%.
WHAT IS PLATINUM USED FOR?
Platinum is widely used in different applications due to its unique chemical and physical properties. Its high resistance to corrosion and oxidation makes it an ideal material for jewelery making, electronic equipment, sensors, laboratory instruments and also in the medical field.
Not everyone knows, but platinum is an important catalyst in many chemical processes, including the production of benzene, sulfuric acid, ammonia and nitrobenzene. It is also used in the production of catalysts for controlling vehicle exhaust emissions, which reduce the environmental impact of vehicles.
Furthermore, platinum is used in the production of components for jet engines and turbines, where its high resistance to corrosion and high temperature makes it an ideal material. Platinum is also used in the production of battery electrodes, oxygen sensors and medical devices such as pacemakers and temperature probes.
Platinum is also an important component in various chemicals and pharmaceuticals, including cleaners, dyes, acids and organic compounds. Furthermore, platinum is used as a construction material in fine jewelry and watchmaking, thanks to its beauty, duration and rarity.
In the medical field, platinum is used as a chemotherapy agent for the treatment of cancer.
WHAT IS PLATINUM USED FOR IN CHEMOTHERAPY?
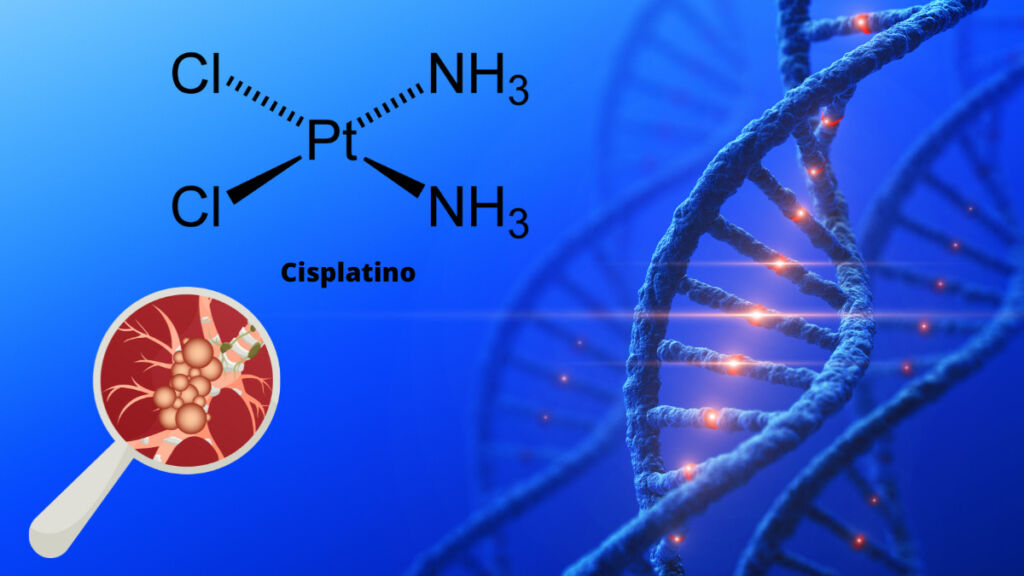
Platinum compounds have long been used as anticancer agents in medicine due to their ability to bind to the DNA of cancer cells and cause their programmed cell death or apoptosis. These compounds are known as DNA alkylating agents, as they modify DNA and prevent cells from replicating and dividing.
The first platinum compound to be used as an anticancer agent was cisplatin, which was developed in the 1960s and was approved for clinical use in the 1970s. Cisplatin is an inorganic compound that binds to DNA through the formation of covalent bonds between its molecules and DNA. This binding alters the DNA structure and interferes with cell replication.
Cisplatin is used in the treatment of various types of cancers, including lung cancer, of the testicle, of the ovary, of the cervix and bladder. However, cisplatin can cause significant side effects, including nausea, He retched, peripheral neuropathy and nephrotoxicity.
This argument was also brilliantly exposed by Emanuele Z. in the article: “PLATINUM vs CANCER”, for the scientific dissemination competition organized by Minerva – Scientific Dissemination Association. I recommend reading!
For that reason, to reduce the side effects of cisplatin, other platinum compounds have been synthesized, come il carboplatino e l’oxaliplatino.
Carboplatin is used in the treatment of ovarian cancer, lung and head and neck, while oxaliplatin is mainly used in the treatment of colon and rectal cancer. Both compounds have been shown to be highly effective in treating these forms of cancer and have fewer side effects than cisplatin.
Furthermore, Other platinum compounds have been developed that aim to improve the efficacy and tolerability of anticancer treatments. For example, nedaplatin is a platinum compound that binds to DNA similar to cisplatin, but which has greater efficacy against small cell lung cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma.
PLATINUM ALLY FOR THE ENVIRONMENT.
Platinum plays an important role in protecting the environment and in the fight against climate change. In particular, the use of platinum in environmental applications is centered on its ability to catalyze important chemical reactions.
As already mentioned, platinum is used as a catalyst in motor vehicle catalytic converters to reduce harmful emissions into the atmosphere, helping to improve the quality of the air we breathe and to lower the environmental impact of transport. The use of platinum in catalytic converters has helped to significantly reduce emissions of air pollutants such as nitrogen oxide (NOx), the carbon monoxide (CO) and unburnt hydrocarbons (HC), dramatically improving air quality around the world.
In addition to the automotive industry, platinum is also used as a catalyst in other manufacturing processes that can have a significant impact on the environment. For example, platinum is used in the production of sulfuric acid, a basic chemical used in many industries, such as the mining and fertilizer industries. The use of platinum as a catalyst in this process has made it possible to significantly reduce sulfur dioxide emissions, a gas harmful to human health and the environment.
Platinum is also used as a catalyst in the production of hydrogen, a clean, renewable energy source that could replace fossil fuels. Producing hydrogen requires an energy source, such as solar or wind energy, which is used to produce electrolysis of water, a process that requires the use of catalysts to increase the efficiency of the process. Platinum is one of the most used materials as a catalyst in this process, thanks to its high catalytic activity and its chemical stability.
Finally, platinum is also used in the production of fuel cells, another technology that can help reduce the use of fossil fuels and related greenhouse gas emissions. Fuel cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity and water, without producing harmful emissions. Platinum is used as a catalyst in fuel cells to increase the efficiency of the conversion reaction.
In conclusion, Platinum is a precious element with several unique physical and chemical properties that make it useful in many fields, from medicine to the automotive industry. However, its rarity and limited geographical distribution can lead to supply problems and high prices. It will continue to be the subject of research and development to find new ways to exploit its properties and meet the needs of modern industry.
SOURCES:
- “Platinum: A Review of Its Use in the Treatment of Solid Tumors”: Zhang C, Xu C, Gao X, Yao Q. Platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy and anti-tumor strategies. Theranostics. 2022 Feb 7;12(5):2115-2132. doi: 10.7150/no. 69424. PMID: 35265202; PMCID: PMC8899578.
- “Platinum-Based Drugs: Past, Present and Future”: Dilruba S, Kalayda GV. Platinum-based drugs: past, present and future. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;77(6):1103-24. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-2976-z. Epub 2016 Feb 17. PMID: 26886018.
- Platinum Group Metals: A Review of Resources, Production and Usage with a Focus on Catalysts: Resources 2021, 10(9), 93; https://doi.org/10.3390/resources10090093
- “The Role of Platinum in Sustainable Development” – “Platinum Metals Review” doi: 10.1595/147106708X325169
- https://www.chemistryworld.com/health-technology/platinum-metal-complexes-in-medicine/3008723.article
- Images ©@gettysignature via Canva.com








Leave A Comment